A FASCINATING IMAGE: Paul Rudolph, sitting on the floor and working—or playing (or both!)—with Legos. He looks to be creating what might be a high-rise residential structure that would express his ideas about how whole apartments could be manufactured and lifted-into-place (as what he called “the brick of the future.”) Around him are numerous boxes of Lego sets (at far left, a pair of them are sitting on a Mies Barcelona chair!), and in the foreground a large number of Lego blocks have already—through Rudolph’s hands—taken on architectonic form.
AND A REVEALING ONE: This photo is also interesting for what else one can detect about Rudolph’s working context. It was taken in one of Rudolph’s work spaces (his office at 54 West 57th Street) and, hung in the background, one can see models of two of Rudolph’s commissions. At the upper-right is a large model of his 1966 design for a resort community at Stafford Harbor, Virginia (and the form of that project’s clusters of housing resonate well with the Lego aesthetic.) Also at the top, just left of center, one can see a “Toio” floor lamp, designed by Achille Castiglioni (which is in the collection of the Museum of Modern Art.) While Italian lighting fixtures are now widely available in the US, when this early 1970’s photo was taken one was much less likely to encounter (and be able to purchase) examples of high-level imported industrial design. To the left of that is a Luxo lamp (which were then ubiquitous in architects’ offices as lighting for their drawing boards.) Image is from a photo print found within the archive of the Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation.
ARCHITECTS MAKE TOYS & TOYS MAKE ARCHITECTS
Architecture is usually a serious matter, as even the smallest construction projects entail large commitments of funds, time, and focus. Moreover, architects and builders must engage with issues of durability, fitness to purpose, the practical constraints of materials and available skills, and conformance with construction regulations that are meant to ensure safety. Anyone who has spent time on construction sites—particularly if it is during a site visit by an architect—quickly realizes that these are venues where frivolity is forbidden, and great tensions are at work.
But there’s also a long engagement between Modern architects and play—specifically: TOYS.
This Toy-Architect relationship operates in two directions:
Architects that have designed toys—both literally, and in the sense that some of their work is toy-like.
Toys that have designed architects—-in the sense that toys having a formative influence on them.
ARCHITECTS AS TOYMAKERS
Architects (and their close associates) have been surprisingly prolific in the creation of toys—and here are some better-known examples:
Though the most famous building toys (A. C. Gilbert’s Erector Set and Frank Hornby’s Meccano) were not designed by architects, at least one of them—Gilbert’s—was inspired by his observation of actual steel girders used in large-scale construction.
But the third most famous building toy—Lincoln Logs—invented in 1916, and still available today—was designed by an architect: John Lloyd Wright. (1892-1972.) He was Frank Lloyd Wright’s son, and—although he had a long and productive career designing a wide range of buildings—he’ll probably remain best known for the creation of this toy.
The Bauhaus was also a source of toy designs, and the challenge of designing them was taken-up by some students.
The most well-known example—and one which has continued to be in production—is a Building Blocks Set designed by Alma Siedhoff-Buscher (1899–1944) while she was a student at the Bauhaus. There were two versions: the first in 1923, with 32 blocks; and a larger set in the following year, with 39. The blocks, of various colors, shapes, and sizes, offer an almost infinite opportunity for creative compositions—figurative, architectural, and abstract—though it is best known with them assembled into the form of a sailboat (which was illustrated on the exterior of the set’s original packaging.)
The flexibility of the Bauhaus style and approach (which allowed it to be applied to challenges as diverse in scale and purpose as architecture, city planning, furniture, textiles, lighting, typography, pottery—and toys!) has never stopped attracting designers—and an ever-widening audience of consumers. Thus, though the Bauhaus has past its centenary, its geometries, motifs, and overall “look” continue to be utilized for every type of design work—even for more recently designed objects of amusement. The growth and victory of this style, and indeed the identity “Bauhaus” itself, is deeply explored in Philipp Oswalt’s incisive book, “The Bauhaus Brand” published by Scheidegger and Spiess—a visually rich and penetrating study of how this “brand” has become omnipresent.
It’s also worth nothing that the same playful. toy-creating spirit can be seen in another of the Bauhaus’s most notable productions: the Triadic Ballet, developed by Bauhaus teacher Oskar Schlemmer (1888–1943.)
The ballet’s costume designs, by Schlemmer—which are more famous than the performance itself (some are shown here)—are perceivable as giant (human sized), moving toy creatures, many of which hew to the geometric Bauhaus aesthetic.
Since models, of proposed buildings, are part of every architect’s practice, doll houses would seem to be a natural arena for their talents—and one of our earlier posts was about a very Modern Rudolphian version of a dollhouse.
The ultimate example of an architect engaged in doll house design was the one created by the final master of the English Renaissance, Sir Edwin Lutyens (1869–1944). His Queen Mary’s Dolls’ House (completed in 1924 for Great Britain’s then reigning queen, and now to be seen at Windsor Castle) was an elaborate affair, and the Royal Collection Trust describes it as including “. . . .contributions from over 1,500 of the finest artists, craftsmen and manufacturers of the early twentieth century. From life below stairs to the high-society setting of the saloon and dining room, and from a library bursting with original works by the top literary names of the day, to a fully stocked wine cellar and a garden, created by Gertrude Jekyll, no detail was forgotten. The house even includes electricity, running hot and cold water and working lifts.”
German Expressionist architect Hermann Finsterlin (1887–1973) is primarily known through his drawings: dreamlike visions of buildings which are often so fantastical that one wonders if they were intended for humans habitation.
Finsterlin also designed charming, colorful toys: some with intersecting geometric forms, and others that are more recognizably architectonic. The latter types were designed as assemblies of smaller parts, which could be disassembled and, presumably, creatively repositioned into new configurations.
Putting “Hermann Finsterlin toys” in Google Images yields a large number of pictures of his visionary drawings, as well as of his equally otherworldly models—but one will also see a some of of his toys. A screen capture (from such an image search), with a number of those toys, can be seen at right.
That most serious of the Modern movement’s master architects, Le Corbusier, did have a playful side, but he’s not generally known to have designed any toys.
But one model—which he used to explain the offset layout of apartments in his Unité d'habitation—is definitely toy-like. Such explanatory aids might seem “cute”—but that quality could well be an architect’s strategic choice, as the interest and even friendliness which models evoke can be effective tools of persuasion. Even so, looking at this intriguing image today, what is also evoked is a Corbusian version of Jenga.
Charles Eames (1907–1978) and Ray Eames (1912–1988), partners professionally and in life, had—and continue to hold—world-wide reputations for their inventive approach to meeting the widest range of design challenges. Working in architecture, exhibit design, cinema, graphics, and—most famously—furniture, their designs are known for what futurist John Naisbitt would call “high touch”: a sense of human, personal interaction (something needed ever more powerfully in the midst of a technological society.) So, even though Eames-designed products (like their celebrated series of chairs) were manufactured by industrial processes, those objects convey a human and often playful spirit—and that was further evident in their design of films and exhibitions.
In 1945, as part of their research into molding plywood into three-dimensional curved shapes, they created a two-part, child-scaled elephant seat. The compound curvatures, entailed in making it, were particularly challenging, and it never went into mass-production during the Eames’ lifetime [but, since 2017, it has been made available by Vitra.]
Also in the play mode is the “House of Cards” set, designed by the Eames and originating in 1952 (with variant and larger versions, issued in subsequent decades.) Enjoyed, and marketed for both adults and children, the cards show a rich assortment of photographs or patterns and objects, and are slotted to allow them to be constructed into a variety of configurations. The card sets continue to be produced, and are also in the collection of the Museum of Modern Art.
The Rudolph family, with young Paul Rudolph at far left. This would have been taken probably shortly before he made the house model.
The archives of the Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation include a letter from Paul Rudolph’s mother, Eurie Stone Rudolph. Internal evidence indicates that it was probably written in the mid-1960s (she makes reference to having visited the New York World’s Fair (1964-1965). The memories of her son, shared in that letter, include young Rudolph creating a miniature house. It is probably mentioned as evidence of his early interest in architecture—but what he built was also something approaching a doll house in scale and detail (though Rudolph would likely eschew that term.).
She writes: “After we moved to Franklin, Paul decided to make a Model house, out of cardboard. It was an ideal home with everything a home could have in it. He made the furniture of first one thing and another. Made lamp bases from marbles, made a Gov. Winthrop Bookcase and little tiny books to go in the case. Made shingles for the house, about one forth inch wide and half an inch long. Made windows, then a friend gave him a little set of electric light[s] for the house. He had it all wired and would turn the lights on to show through the windows. When we moved to Athens [Alabama} we moved that six foot house as Paul did not want to give it up. It had given him a lot of pleasure to show it to people as they always seemed so interested in that he had made everything.” [The full text of this fascinating letter can be found in the catalog of the Paul Rudolph centenary exhibit.]
One notable point about many of the above toys (and also the one we’ll discuss below) is that they’re systems. A toy model set that allows one to construct a single type of thing (for example, of the Space Shuttle) is a system: a kit of parts that makes a whole. But most of the toys above are what Christopher Alexander called a generating system: a kit of parts that allows one to make multiple wholes. Built-in to generating systems is flexibility of arrangement and the freedom to invent new configurations. When this quality is found in a toy, that’s perfect for encouraging an exploration of (and sensitivity to) the possibilities of design.
FROEBELIZATION — TOYS CREATING ARCHITECTS?
The most famous connection between toys and Modern architecture goes in the other direction: not architects making toys, but rather: toys making architects. We speak, of course, about the Froebel Blocks. Friedrich Wilhelm August Fröbel (or Froebel) (1782–1852) was a German educator, active in the first half of the 19th Century. He was one of the creators of the modern recognition that children have unique needs and capabilities, created the concept of the kindergarten (including creating the word), and designed a comprehensive set of educational toys known as “Froebel gifts”. They were primarily composed of a series of progressively more sophisticated sets of blocks. Frank Lloyd Wright was given a set, shortly before he turned ten years old, and in his autobiography wrote:
“For several years I sat at the little kindergarten table-top ruled by lines about four inches apart each way making four-inch squares; and, among other things, played upon these ‘unit-lines’ with the square (cube), the circle (sphere) and the triangle (tetrahedron or tripod)—these were smooth maple-wood blocks. All are in my fingers to this day.”
—and—
“The virtue of all this lay in the awakening of the child-mind to rhythmic structures in Nature… I soon became susceptible to constructive pattern evolving in everything I saw.”
What could be constructed from the blocks—and what creativity might it induce in a child? Wright clearly thought they were influential on him—and the fact that Le Corbusier and Buckminster Fuller were also exposed to the Froebel system is suggestive of a fruitful connection between this type of education and the formal results emerging when (and if) the child becomes a professional designer. Ultimately, such cause-and-effect remains in the realm of speculation—but it has received the deep exploration in the late Jeanne S. Rubin’s book: “Intimate Triangle: Architecture of Crystals, Frank Lloyd Wright and the Froebel Kindergarten".
The other scholar of this topic—perhaps world’s greatest expert on architectural toys—is Norman Brosterman, an architect, curator, historian, and writer. His collection (including building sets like the Froebel system) was acquired by the CCA - the Canadian Centre for Architecture. Several exhibits have focused on toys from that collection, and several books on the topic, by Brosterman, have been published: “Potential Archicture,” “Building in Boxes,” and “Inventing Kindergarten.”
Architectural historians have made-the-case that it would not be a great leap to go from the compositional possibilities offered by the Froebel sets of blocks -to- the designs of Wright. Brosterman and others have offered some visual evidence—as in this paring of images from one of his books (shown here.)
RUDOLPH AND LEGO
Although it ceased regular publication two decades ago, and has faded from public consciousness, LIFE magazine had been—for nearly 2/3 of a century—one of the titans of US magazine publishing and was part of the consciousness of every American. With a circulation of millions of copies-a-week, the famous LIFE logo—bold sans-serif letters within a red rectangle—became synonymous with the best in photojournalism: LIFE’s photographers and reporters delved into every aspect of the human experience and nature—from the playful -to- the most somber, from peaceful creativity -to- the darkest tragedies of war. With its enormous circulation and respect, anything—or anybody—that got published in LIFE was lifted to national attention.
LIFE’s December 15, 1972 Special Double Issue on the Joys of Christmas looked at the holiday from a variety of viewpoints, utilizing the photo-essay format for which the magazine was celebrated. The issue included articles about Bethlehem, holiday preparations and celebration on an American farm, a timeline of historic events that have happened on Christmas day, ongoing acts of charity from around the country, and examples of artistic and ornamental Christmas baking.
Among this smorgasbord of holiday celebration is an article that—even if there wasn’t an explicit Christmas connection, certainly carries a mood of joy: “Masterminds At Play”. On the magazine’s Contents page, the editors expressed their intent in this way:
“Some ingenious grown-ups get a chance to see what they can do with children’s playthings.”
And, in the article’s introductory text, they further explain:
“As every child who has grown-up within grabbing distance knows, toys fascinate adults. With a sympathetic nod to the kids, therefor, LIFE asked four particularly inventive adults to indulge their impulses and have a good time with gadgets usually only get a chance to play with.”
Their choice of creative adults was stellar—each masters in their own field: custom car designer George Barris (whose most famous work was the 1960’s TV version of the Batmobile), artist Norman Laliberte (whose colorful banners suffused the Vatican Pavilion at the New York World’s Fair), writer Lonne Elder III (known for his script for the classic film, “Sounder”), cinematic master Federico Fellini—and Paul Rudolph.
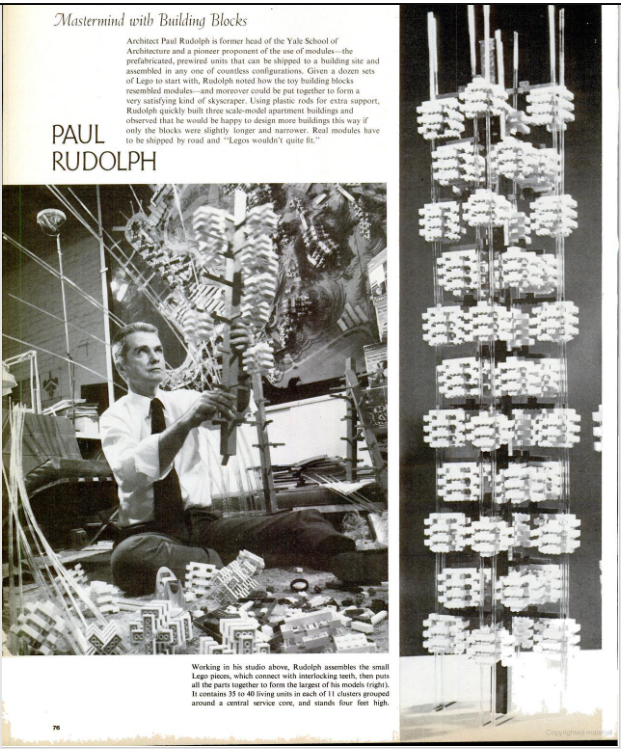
While Fellini clowned with some children’s makeup, and Elder wrote a brief play for a pair of marionettes, Rudolph worked with LEGO blocks—many sets of them (we counted at least 8 boxes of Legos in one photo Rudolph at work with them.). As the article’s text mentions, he supplemented the blocks with plastic rods. [Rudolph associate Ernest Wagner tells us that Paul Rudolph liked to explore the industrial surplus and plastic supply stores which could then be found on downtown New York’s Canal Street—and such venues would likely have been them source of those rods.]
We’ve reproduced Rudolph’s page below—and, in case the texts are hard to read, we’ve transcribed them for you. The introduction on Rudolph’s page explains:
Mastermind with Building Blocks
Architect Paul Rudolph is former head of the Yale School of Architecture and a pioneer of the use of modules—the prefabricated, prewired units that can be shipped to a building site and assembled in any one of countless configurations. Given a dozen sets of Lego to start with with, Rudolph noted how the toy building blocs resemble modules—moreover could be put together to form a very satisfying kind of skyscraper. Using plastic rods for extra support, Rudolph quickly built three scale-model apartment buildings and observed that he would be happy to design more buildings this way if only the blocks were slightly longer and narrower. Real modules have to be shipped by road, and “Legos wouldn’t quite fit.”
And the caption reads:
Working in his studio above, Rudolph assembles he small Lego pieces, which connect with interlocking teeth, then put all the parts together to form the larges of this models (right). It contains 35 to 40 living units in each of 11 clusters grouped around a central service core, and stands four feet high.
WHY LEGOS?
Of course, with it’s brick-like construction system and pieces, it would be natural to associate Lego with architecture. Over the decades, there have been numerous examples and exhibits of architects and designers using Legos, either attempting to recreate well-known buildings, or to explore new architectural designs.
For about the last decade, the Lego company has proclaimed a connection between their system and iconic architecture by issuing sets of blocks which are constructible into some of the most famous Modern architectural works of the 20th Century, among them: the Le Corbusier’s Villa Savoye, Utzon’s Sydney Opera House, SOM’s John Hancock Building, the United Nations headquarters—and even Mies van der Rohe’s Farnsworth House.
Wright seems to be a favorite, in that he’s the only architect that they’ve chosen who has the honor by having several of his buildings done as Lego sets: the Robie House, the Imperial Hotel, the Guggenheim Museum, and Fallingwater—the last one of which seems to work especially well with the Lego system.
But why did LIFE magazine connect Rudolph and Legos? Were the editors already aware of Rudolph’s oeuvre, and noticed the visual resonance between some of his projects and the Lego system? Or did they approach Rudolph, telling him the premise of the article, and ask him what he’d like to “play” with?
RUDOLPH, MODULARITY, aND “THE BRICK OF THE FUTURE”
We’ve seen no records about how Paul Rudolph’s participation in the LIFE article came about—but its text does point to a topic which was of ongoing and intense interest to Rudolph: what he called “the brick of the future” (which he also sometimes called “the twentieth century brick.”)
Those are Rudolph’s terms for a future possibility for architecture and the construction industry: entire apartments would be made off-site in factories, and then transported to the construction site. The construction site would have structures to receive these modules, and the apartment units—like modular bricks—would be lifted into their final locations and connected to utilities.
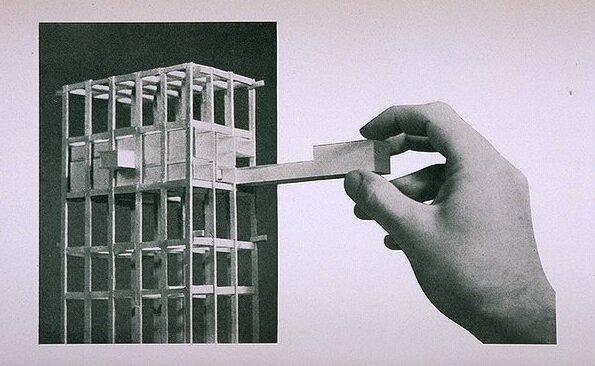
Generally, Rudolph envisioned that “brick of the future” apartment houses would be in the shape of towers—sometimes quite tall—and that’s what his design in the LIFE article looks like (see enlargement from the article, at right). But Rudolph also had additional possible configurations in mind: mid-rise stepped assemblies, and low-rise (two or three stories) versions, where the units would spread across a landscape.
Rudolph’s liking for, and interest in modular (or modular-like) “brick”-unit forms can be seen across most of his 50-year career—it is one of his major architectural, technological, aesthetic, and policy commitments—of which he explicitly and repeatedly spoke, and tried to bring to fruition in numerous projects.
Sometimes this affinity comes out of aesthetic considerations. Rudolph, well-aware of all chapters in the history of Modern design and art, would have digested the artistic genome of overlapping and projecting rectilinear forms. This type of design was manifest in the architecture and sculpture of the early decades of the Modern movement—and superb examples can be seen in this pair of sculptures by De Stijl artist George Vantongerloo (1886-1965) shown here (and one can easily imagine them being constructed out of Legos!) Also, creating compositions like this was a standard exercise in Modern, Bauhaus-derived design education programs—and remains so in some schools today. Even more pertinent, it’s worth remembering that Rudolph was a student, at Harvard, of Walter Gropius—the former director of the Bauhaus.
One can see this artistic, sculptural approach, using module-like forms, in his 1960 project for O’Brien’s Motor Lodge (shown below), and in his 1963 design for the Orange County Government Center.
Of the O’Brien project, Rudolph himself later connected it to his modular concerns, saying:
“In a sense this is an earlier study of the formal architectural possibilities of the large scale, three-dimensional, pre-fabricated unit (Twentieth Century Brick), but constructed by traditional methods of brick and concrete.”
One can also see his idea to use modular, brick-like apartments used—not just as a form, but explicitly as a construction system—in a design from about the same time: his 1959 project for a Trailer Apartment Tower (see Rudolph’s sketch at right). He said of this proposal:
“For a number of years now I have felt that one way around the housing impasse would be to utilize either mobile houses or truck vans placed in such a way that the roof of one unit provides the terrace for the one above. Of course the essence of this is to utilize existing three dimensional prefabricated units of light construction originally intended as moving units but adapted to fixed situations and transformed into architecturally acceptable living units. One approach would be to utilize vertical hollow tubes, probably rectangular in section, 40 or 50 stories in height to accommodate stairs, elevators and mechanical services and to form a support for cantilever trusses at the top. These cantilever trusses would give a ‘sky hook’ from which the three dimensional unit could be hoisted into place and plugged into its vertical mechanical core.”
PAUL RUDOLPH’S MODULAR PORTFOLIO
Looking through Rudolph’s oeuvre, one can see that the modular, LEGO-like approach comes up repeatedly. In addition to the projects shown above, below we’ll look at 4 others which evidence his ongoing interest in this such a construction/design system.
1967 - GRAPHIC ARTS CENTER
Designed to be placed on the Western edge of Manhattan island (slightly north of the site of the World Trade Center), the Graphic Arts Center was a to be a large complex that would include housing (4,000 apartments!), offices, manufacturing, shops, schools, a marina, and other facilities. Rudolph describes his intent—including the use of a modular building approach:
“The proposals for the Graphic Arts Center are based on the concept of the megastructure, or the idea that many functions can be served in a single large building complex. In this case there are facilities for industry (lithography, legal and financial printers); office space; 4,000 apartments of varying kinds; elementary schools, kindergartens; play spaces at grade, as well as on platforms in the sky; community center; restaurants; commercial shopping; gardens and recreational space; and parking-trucking access incorporating portions of the West Side Highway. In other words, it is a city within a city. The idea of a megastructure is different from the idea of building an apartment house, industrial and office space, schools and restaurants. Rather, it is the intent to build all of these multiple functions in one complex.”
“The apartment houses are, perhaps, conceptually the most interesting, since they propose to utilize techniques developed by the mobile house industry (this industry now accounts for one out of five new housing starts in the United States and the graph is steadily going upward). These units would hang from trusses supported on masts which contain elevator and stair cores, plus vertical lines of utilities. By arranging the mobile house units in “log cabin” fashion, the roof for one becomes the terrace for the one above.”
A model of a one of the towers of the Graphic Arts Center. One can see the connection to Rudolph’s other modular-oriented designs, as well as the model he later made for the LIFE article.
A portion of Paul Rudolph’s large model of the proposed Graphic Arts Center (which was to be built in lower Manhattan) in which one can get an idea of the project’s immense scale.
1968 - ORIENTAL MASONIC GARDENS
Prefabrication was part of the architectural zeitgeist of the 1960’s, and the US government—through their “Operation Breakthrough”—sponsored a large number of experiments in an attempt to find out if industrialized housing was a viable approach for creating housing. That was the context for Oriental Masonic Gardens, a federally-aided project designed help solve housing shortages in New Haven. Rudolph’s design included 2-to-5 bedroom apartments, and consisted of 148 units on 12.5 acres. The housing was made of pre-fabricated units (a total of 333 modules), which were brought to the site and arranged in a two-level configuration (which gave each residence a private yard).
Bedeviled by issues of construction quality, this forward-thinking experiment was eventually demolished in 1981. Rudolph acknowledged the problems of the project, but continued to think that this approach—prefabrication—contained the possibility of positive solutions to creating housing that was economical, but which also allowing for formal and spatial variety.
Oriental Masonic Gardens’ modules, whose designs allowed for a variety of differently sized housing options, were manufactured off-site and then craned into place.
The homes were duplexes, and were placed in cruciform configurations. Even though they were contiguous, each home in these 4-unit clusters had their own separate yard.
1967 - LOMEX: THE LOWER MANHATTAN EXPRESSWAY
The Lower Manhattan Expressway (LOMEX) was a project to connect bridges (that were located on the opposite sides of Manhattan island) with a new throughway. The existing streetscape would not allow for high-speed movement between those two points, and so a new, borough-spanning solution was called for. Rather than this being just a matter of highway engineering, Paul Rudolph approached it comprehensively: his design embraced multiple modes of transportation, housing, offices and other facilities—-all within a dramatic megastructural vision that took on varying shapes and heights to accommodate different functions.
A key aspect of Rudolph’s design was the use of prefabrication for the high-rise housing. Vertical structures (which had, built-into them, elevators, stairs, and utilities like plumbing and electricity) would be erected; and then apartments—modular units manufactured off-site—would be trucked-in and slotted into place. Here again, this modular system could be flexible, with the units arranged in different configurations, and on structures of varying heights.
Paul Rudolph’s perspective rendering of LOMEX, which would have spanned all across Manhattan. In the distance (to be located at Manhattan island’s edges) can be seen high-rise residential towers that are part of the project—and they were to use the pre-manufactured “brick of the future” housing system that Rudolph envisioned.
Rudolph’s drawing, illustrating an aspect of the LOMEX project’s high rise housing system. Housing modules—the “brick of the future”—would be manufactured off-site, and delivered to the site by truck (see bottom of drawing.) They would then be craned upward, and set into permanent place on the building’s structural system.
1980 - THE COLONNADE
Rudolph intended these luxury condominiums, The Colonnade in Singapore, to be built using the modular, “brick of the future” approach that he’d been investigating and trying for decades. For reasons of timing and local economics, it ended up being built with more conventional construction methods—but one can see, both in Rudolph’s drawings and in the final result, that the form of the concept was retained. Rudolph’s original intent still may have potential for the construction of buildings like this.)
Shown is a portion of one of Rudolph’s drawing for The Colonnade: an isometric rendering, showing the exterior, with highly articulated volumes, grid-like horizontal and vertical structural elements, and a profusion of balconies. The modular intent is clearly manifest in this vision.
Apartments in The Colonnade are among the most sought after in Singapore. Even though it was ultimately built using conventional methods, its as-built presence still conveys Rudolph’s original concept of it being constructed with pre-fabricated units.
RUDOLPH’S FURTHER APPLICATIONS OF MODULARITY
Rudolph’s interest in, and attempts to apply the principle of flexible modularity, was not limited to building-scale projects. He also brought this approach to the design of construction systems, furniture, and lighting—and here are examples of each:
1960’s - RIBBED CONCRETE BLOCK SYSTEM
Rudolph’s most famous building is his Yale Art & Architecture Building, well-known for its ribbed concrete surfaces. To achieve that finish, the concrete was cast-in-place and then bush-hammered by hand. Rudolph liked the shadowed-/textured effect that the ribbing created, and used it in other buildings which he designed (i.e.: Endo Labs and the Boston Government Service Center). But that construction method proved too expensive to use in some projects, and Rudolph and his staff sought an alternative which would produce visually similar results.
For Crawford Manor, a 109 unit high-rise apartment building for elderly residents in The Bronx, NYC, they designed a set of concrete blocks with vertically ribbed surfaces. The system would still give the serrated effect that Rudolph wanted, but which would be significantly less expensive to construct. A variety of shapes. to accommodate different construction conditions, were designed—a Lego-like “generating system”. Construction began in 1964 and finished in 1966.
In addition to the cost savings. the ribbing visually “broke down” down the scale of concrete block (so as to avoid an unwanted monolithic look to the building), and it also prevented run-off stains: water is channeled into the interstices while the front of the block is exposed to cleaning. Rudolph’s modular ribbed concrete blocks were later used in several of his other buildings, such as the Chorley Elementary School and UMass Dartmouth.
A drawing, from Paul Rudolph’s office, showing precast and ribbed concrete blocks (as used at Crawford Manor). The version show (straight, with ribbing on both sides) would be only one of the set of shapes produced for this residential high-rise..
In this photo, one can see a variety of construction conditions (flat surfaces, curved surfaces, exterior and interior corners) for which different shapes of pre-cast ribbed concrete blocks were designed and manufactured.
1970’s - FURNITURE SYSTEM
Paul Rudolph designed his own Manhattan residence: his “Quadruplex” penthouse, near the United Nations. Rudolph often included built-in seating in his projects, and that’s very much part of this penthouse’s design. But he also wanted free-standing, movable furniture, and could not find any existing (to purchase) that met with his approval—so he created his own.
Rudolph came upon a system of connectors and metal tubes (“nodes and struts”) which was often used in retail settings to create display shelving. This was—like Lego—truly a “generating system.” Seeing the immense flexibility which the system offered, Rudolph proceeded to design (and have fabricated) a variety of furniture for his home. [Authorized editions of these designs continue to be offered, via the Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation.]
Among the purposes, for which Rudolph utilized the connector and tube system, was to create a display stand for an original Louis Sullivan panel which he owned (and that he placed in the Quadruplex’s living room.)
In addition to a rolling dining chair (shown above), Rudolph also created a rolling lounge chair, and as well as side-tables. The chairs are now being made available through the Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation.
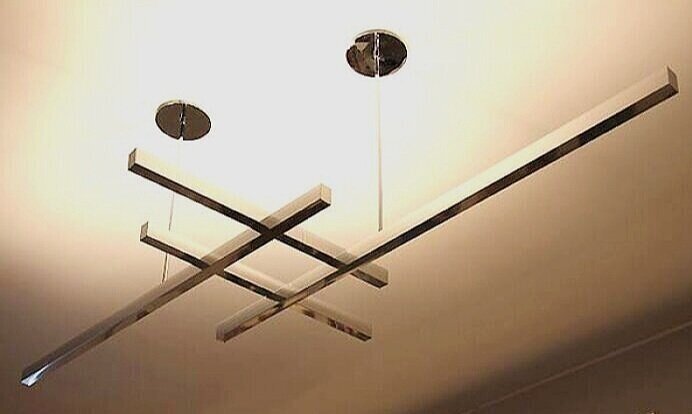
1970’s - LIGHTING SYSTEM
It’s fair to say that Rudolph was obsessed with light: both natural and artificial, and the effects that could be created with it. Through most of his career he designed custom lighting for his projects—and because he used standard electrical components (and sometimes industrial surplus), these inventive fixtures could also be inexpensive.
This interest in light fixture design evolved further. Architectural historian Timothy M. Rohan, in his monograph on Rudolph, writes:
Although he cared little for the everyday workings of business, Rudolph could be quite entrepreneurial. In 1976, Rudolph and[Ernst] Wagner founded Modulightor, a firm that sold lighting. . . .”
The system which Rudolph came up with used a limited number of parts and shapes—but, very much like Lego, this generating system of components could be arranged and assembled to create a vast range of light fixtures: sconces, art lighting, wall washers, chandeliers, task lights…. Rudolph not only designed the system, per se (which was simultaneously economical in approach, yet allowed for broad creativity), but he also designed a large line of fixtures which utilized the system. The Modulightor company continues to offer fixtures, using his approach.
Rudolph showed that, even with a limited set of shapes, an immense range of configurations are possible. This is manifest in abundance in the lighting system available from Modulightor—a firm he co-founded with Ernst Wagner. Shown are a few examples of the types and shapes of light fixtures that can be built from the generating system that Rudolph invented.
IMAGE CREDITS
Lincoln Logs: John Lloyd Wright, courtesy of Wikimedia Commons; Triadic Ballet: Fred Romero, courtesy of Wikimedia Commons; Queen Mary’s Dolls’ House: Rob Sangster, courtesy of Wikimedia Commons; Le Corbusier Model: from Le Corbusier, Oeuvre complète (Zurich, 1950), vol 4, p 186, collection Canadian Centre for Architecture, Montréal; Eames Elephant: Sinikka Halme, courtesy of Wikimedia Commons; Eames House of Cards: SebastianHelm, courtesy of Wikimedia Commons; Rudolph Family: © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, The Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation; Frobel Blocks Set: Kippelboy, courtesy of Wikimedia Commons; Froebel Student Using Blocks: Maria Kraus-Boelte/John Kraus: The kindergarten guide: An illustrated hand-book. 1877, courtesy of Wikimedia Commons; Vantongerloo Sculptures: http://sdrc.lib.uiowa.edu/dada/Classique_Baroque/pages/033.htm, courtesy of Wikimedia Commons; O’Brian’s Motor Lodge: © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, The Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation; Trailer Apartment Tower: © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, The Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation; Graphic Arts Center Model in Rudolph Office: © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, The Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation; Graphic Arts Center Model: © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, The Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation; Oriental Masonic Gardens Construction Photo: © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, The Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation; Oriental Masonic Gardens: © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, The Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation; LOMEX Perspective: © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, The Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation; LOMEX Construction Diagram: © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, The Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation; Colonnade Drawing: © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, The Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation; Crawford Manor Block Drawing: © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, The Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation; Crawford Manor Photograph: Photo by Kelvin Dickinson, © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, The Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation; Sullivan Panel: © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, The Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation; Rolling Chair: Courtesy of Peter Aaron; Modulightor Fixtures: Courtesy of Modulightor