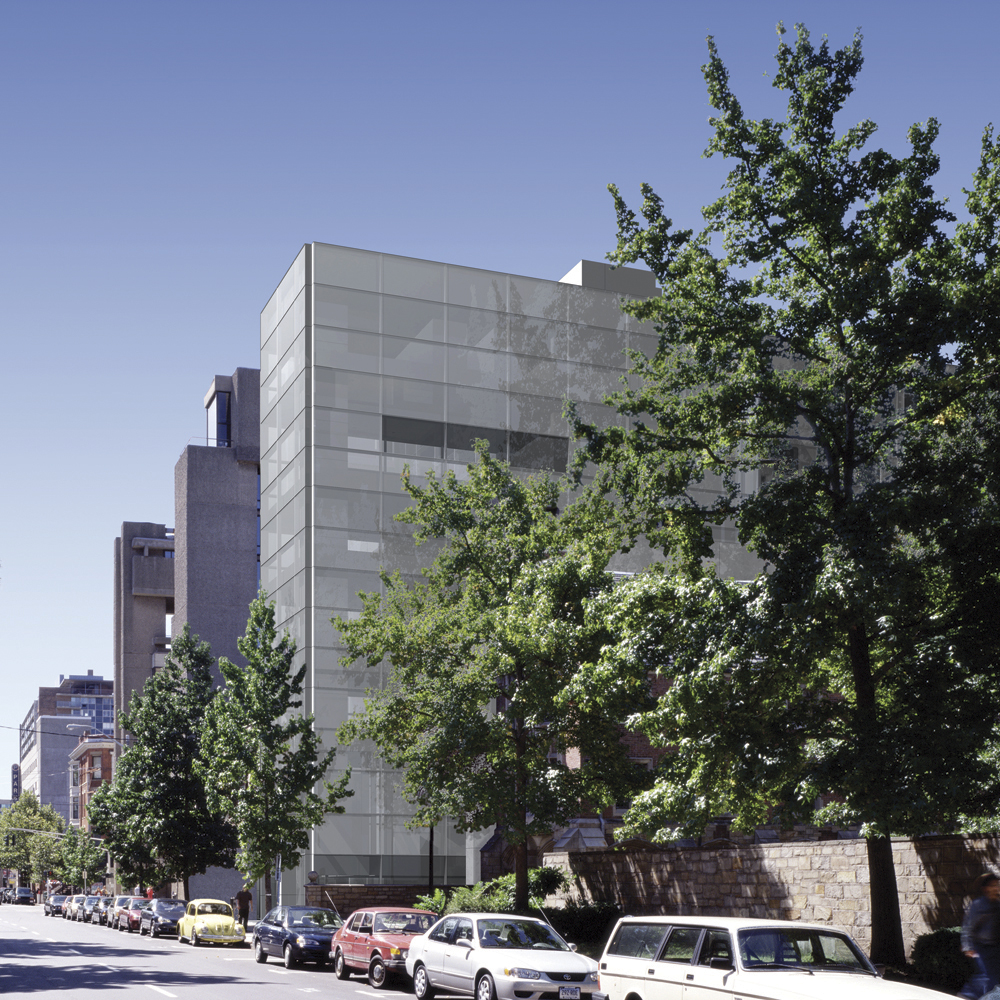
The great fashion designer Halston, enthroned in his living room—within the famous “101”, the townhouse in New York’s Upper East Side neighborhood in Manhattan . Photo by Harry Benson, from a feature on Halston in Life Magazine.
UPDATE:
The below was written as Netflix was planning its 2021 series ‘Halston’ Since its gone live there has been a HUGE amount of interest about the designer and especially his legendary residence at 101 East 63rd Street in New York City.
We’ve noticed a lot of familiar photos of the interior circulating on social media and even some articles which have published incorrect information about the space.
We were hoping the series was going to rebuild the interior of the home on a soundstage, but appreciate the effort made by the production team to make a property in Brooklyn look as similar as possible (we do regret the handrails that Rudolph never used but understand why they are needed!).
A lot of articles mention Tom Ford’s 2019 purchase and his plans to restore the interiors. For those of you who want to know more, we are republishing the below:
A House with a History
Paul Rudolph designed the original residence at 101 East 63rd street for Mr. Alexander Hirsch in 1966. He created a Modernist oasis for his client, an intensely private person who wanted a place to escape to while still being in the heart of Manhattan. As Rudolph later described the project in Sibyl Moholy-Nagy’s 1970 book, The Architecture of Paul Rudolph:
A world of its own, inward looking and secretive, is created in a relatively small volume of space in the middle of New York City. Varying intensities of light are juxtaposed and related to structures within structures. Simple materials (plaster, paint) are used, but the feeling is of great luxuriousness because of the space. The one exposed facade reveals the interior arrangement of volumes by offsetting each floor and room in plan and section.
The house later went from being a private refuge to a celebrity hot spot known for its notorious parties when it was sold to the fashion designer Halston in the 1970’s. Halston himself spoke about the space in a recent documentary about his life that was featured on CNN:
I’m Halston and this is my home. The architect was Paul Rudolph and the day I saw it, I bought it. Its the only real modern house built in the city of New York since the second world war. Its like living in a three dimensional sculpture.
A video portion of Halston walking through 101 East 63rd from the CNN documentary. Halston’s description of the house begins at 0:46:50.
His lawyer upon visiting the house quipped, “I’m going to enjoy making money for you Halston because you know how to spend it.”
For more information about the house, you can find drawings and photos of it on our project page here.
Perspective Section Rendering. © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation
A Buyer as Famous as the House
As we reported in a previous blog post back in March, the house was finally sold to fashion designer Tom Ford after being on the market for a number of years. The sale, first reported in an article in Women’s Wear Daily after being the subject of rumors for a few weeks, was reported across social media and the design community. Articles appeared in Garage, Vogue, GQ, Mansion Global, the Daily Mail and New York Times.
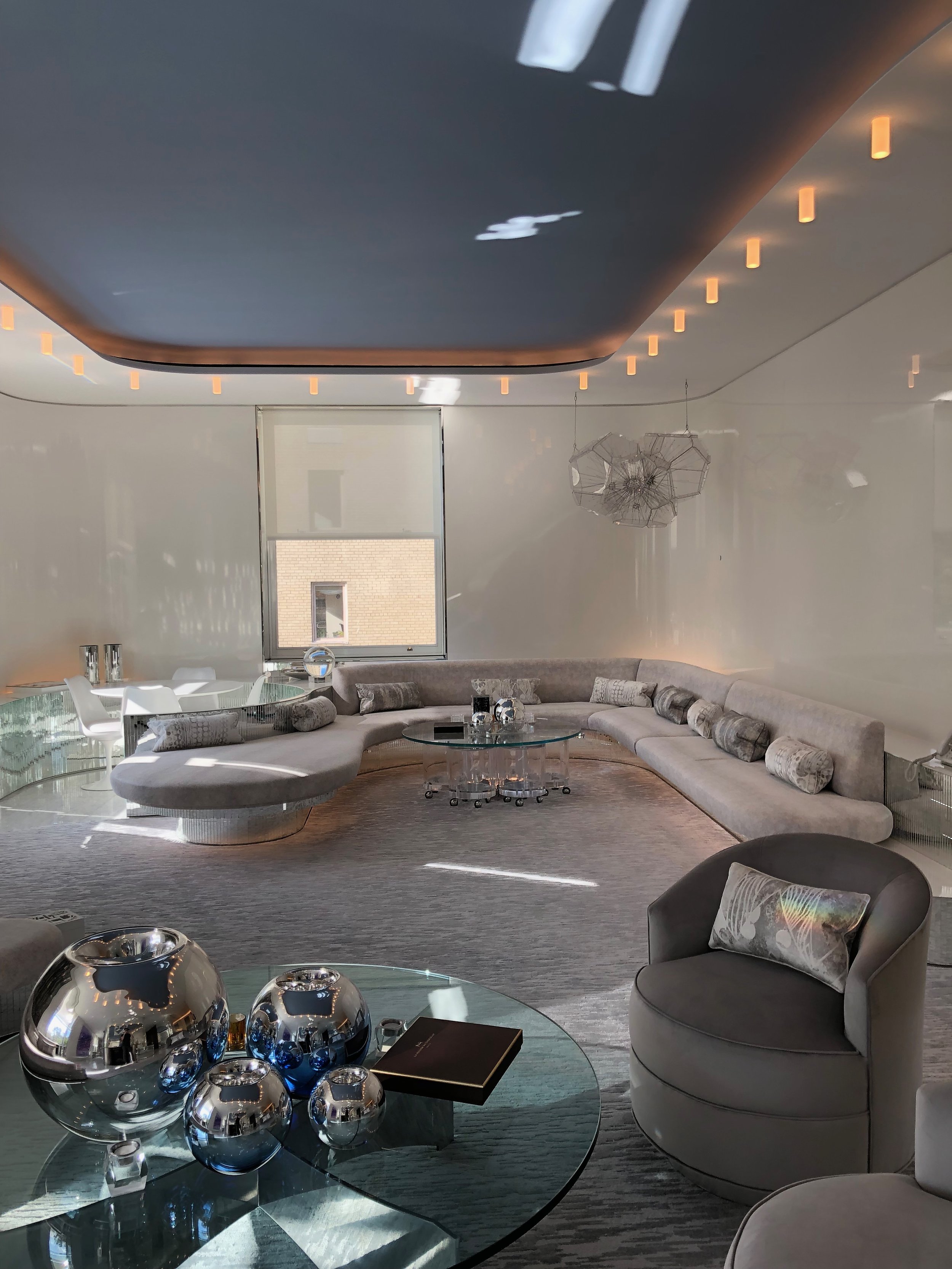
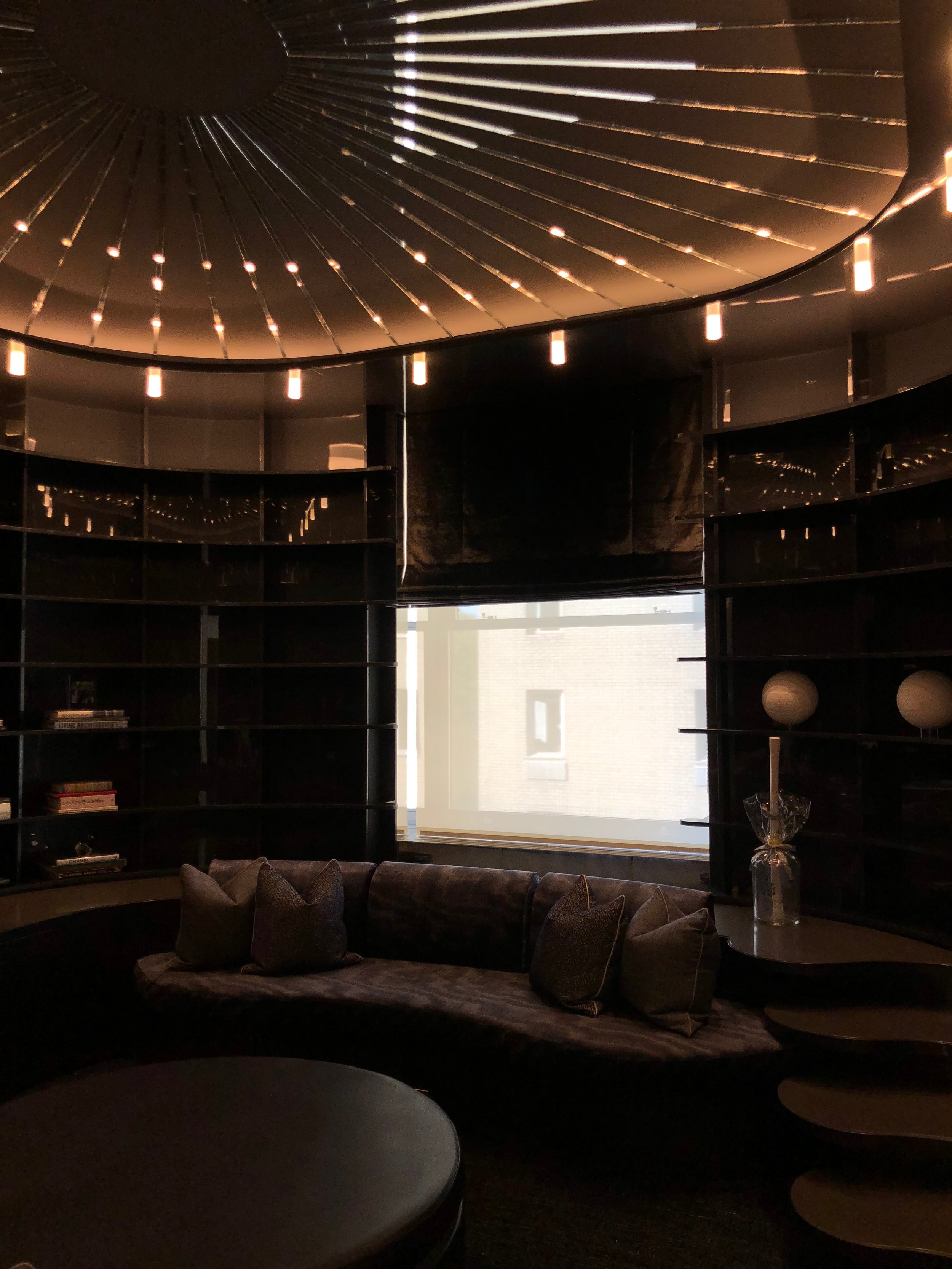
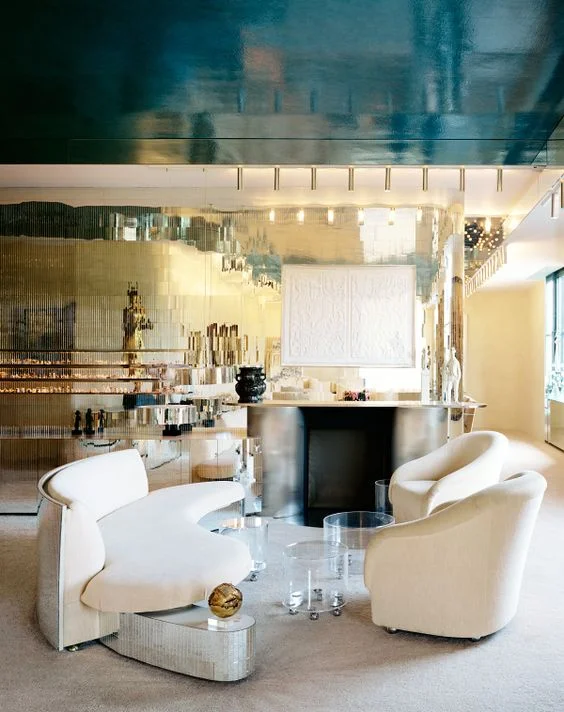
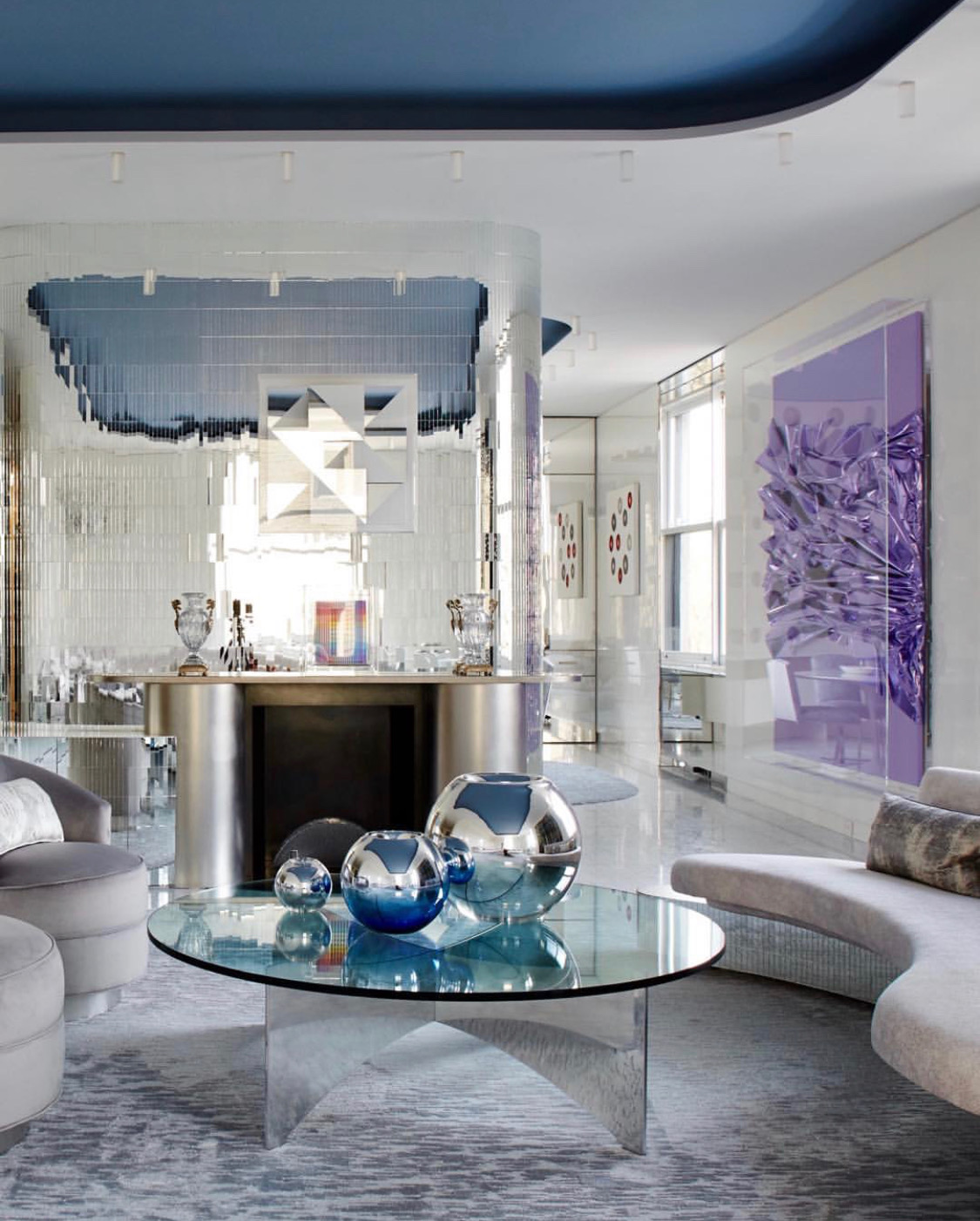
Halston had hired Rudolph to renovate the space when he bought it. Wall to wall grey carpet, mirrored and Plexiglas furniture and chain-mail curtains were installed as a result. Members of the design community were pleased to learn that Tom Ford intended to restore the interior to the glamour that many remembered.
A Restoration, or Renovation?
Shortly before the sale was announced, The Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation was approached by Mr. Ford’s architect, Atmosphere Design Group, to obtain copies of Rudolph’s original drawings. We were told ‘the client’ wanted to restore the interiors.
Paul Rudolph’s Mezzanine Floor Plan. © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation
Paul Rudolph’s Third Floor Plan. © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation
We asked the architect to consider consulting with the Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation during the design process to ensure the design was faithful to Mr. Rudolph’s original vision. They said they would consider it and were never heard from again. Given the architect is generally known for Mr. Ford’s retail store design, we were concerned when we learned a demolition permit was issued in August, 2019.
Our request was not without precedent - the Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation has given advice, free of charge, to owners of Rudolph-designed properties in the past. We were part of the design review of proposed replacement windows at the Mary Jewett Arts Center. We also helped a home owner in New Jersey find an architect to design an addition. In the end, he was able to hire Rudolph’s original project manager to construct the addition in way that fit into the original design.
A Cautious Optimism
We continued to hold out hope that - despite not hearing from the architect - the project was ‘in good hands.’ From online comments and at our public events, people were relieved to hear Mr. Ford had purchased the property as he was known for taking care of homes designed by significant architects, such as Richard Neutra.
Following the CNN documentary, Netflix announced that it too was going to do a story about Halston and were scouting locations to use for filming. Netflix location scouts visited us in the Rudolph-designed apartment at Modulightor and we spoke to them about Mr. Ford’s proposed changes and they said they would call us after seeing the original home for themselves. That was followed by the New York Times publishing the Halston interior as #19 on its ‘25 Rooms that Influence the Way We Design’
As the iconic interior continued to be in the news, we waited to see what was being done to the space.
Then we got a call - “The space is gutted, Its unrecognizable.”
What Will Change and What Will Stay the Same
The foundation immediately made phone calls and was able to obtain a set of the permit drawings. The following is what we learned about the work:
First Floor - Existing Plan. © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation
First Floor - Demolition Plan. Drawing by Atmosphere Design Group, from the NYC DOB.
First Floor - Construction Plan. Drawing by Atmosphere Design Group, from the NYC DOB.
Second Floor - Existing Plan. © The Estate of Paul Rudolph, Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation
Second Floor - Demolition Plan. Drawing by Atmosphere Design Group, from the NYC DOB.
Second Floor - Construction Plan. Drawing by Atmosphere Design Group, from the NYC DOB.
What’s different:
All of the bathrooms are being gutted and some are combined to become larger. Looking at the elevations, we are pleased to learn it will include floor to ceiling mirrors with chrome vanities and toilets in some of them.
Mirrors, mirrors everywhere… reminds us of the note ‘melamine everything’ that was found during a renovation of Rudolph’s own 23 Beekman Place. We especially love the polished chrome toilet and vanity with undercounter lighting. Drawing by Atmosphere Design Group, from the NYC DOB.
The Kitchen will be enlarged (presumably for a menu greater than just ‘baked potatoes’)
Mirrors used for the kitchen back-splash are reminiscent of the kitchen designed by Paul Rudolph at the Modulightor’s duplex apartment. Drawing by Atmosphere Design Group, from the NYC DOB.
The Master Bedroom’s walk in closet is being removed and turned into a separate bedroom
What’s the same:
The main space for the most part is left alone. While this is a relief, it will disappoint anyone who was hoping the hardwood flooring, installed by a previous owner, would be replaced by Halston’s signature grey wall-to-wall plush carpeting.
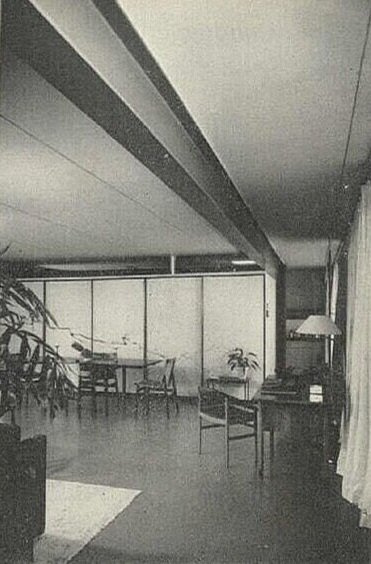
The iconic living room will be left mostly as is. The furniture layout suggests it may be recreated to match Halston’s Rudolph-designed originals. Drawing by Atmosphere Design Group, from the NYC DOB.
The living room floor and stair treads are now wood. According to the plans, they will remain wood. Photo by Carl Bellavia, Archives of the Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation.
The original funriture layout designed by Paul Rudolph for Halston. Photo by Harry Benson, from a feature on Halston in Life Magazine.
What could be a concern:
Despite being in a landmark district - and signed off by the Landmark’s Commission as having no affect on the building exterior - the drawings show the original garage door will be removed and replaced.
Note the garage door is dotted on the demolition plan, with a note calling for it to be replaced. Drawing by Atmosphere Design Group, from the NYC DOB.
The drawings call for renovations of the landscaping and roof to be filed separately
The Fourth Floor construction plan, showing no work to be done on the roof, but calling for new roof tree planters. Drawing by Atmosphere Design Group, from the NYC DOB.
The Paul Rudolph Heritage Foundation will continue to watch for future applications to see what is planned for these areas that fall under landmarks review and protection.













![Paul Rudolph’s early perspective rendering of the arts center building [the medium appears to be colored pencil on a diazo “whiteprint”]—possibly done as a presentation drawing for the client and/or other stakeholders. While there would be changes made (between what’s shown in this drawing and the final design) this shows that the overall form and organization of the building has been well established.](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/5a75ee0949fc2bc37b3ffb97/1620676728796-X6SBHNY2YT0GVE8T4R4I/color+rendering.jpg)
















![A chart from the Pew Research Center’s study of Public Trust in Government: 1958-2019 The overall downward trend, from 1964 to the present, is evident. [Note that the largest and steepest drop was in the wake of the mid-1970’s Watergate scandal.] Wh…](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/5a75ee0949fc2bc37b3ffb97/1616438220772-C9X7PWXIHIW0L7MK9ZX1/trust%2Bin%2Bgovt.jpg)
























































